Transfer learning Gaussian process regression surrogate model with explainability for structural reliability analysis under variation in uncertainties
Abstract
In this paper, a Gaussian process regression surrogate model with transfer learning (TL-GPRSM) is introduced to reduce the computational cost of structural reliability analysis by using the input–output relationship of the source analysis having similarities with that of the target analysis. In addition, automatic relevance determination (ARD) is introduced for providing the explainability of the constructed model and confidence assurance of transfer learning. Two verifications were conducted: (i) the surrogate modeling of the live-load performance analysis of a steel bridge with corrosion by applying the source analysis in the undamaged condition and (ii) seismic performance analysis of a bridge pier, which required nonlinear time-history analyses for various earthquake loads. The results showed that TL-GPRSM was especially effective in surrogate modeling of the performance analysis with linear numerical calculations. Moreover, it was shown that the effectiveness of transfer learning in each modeling and explainability of the constructed model could be discussed based on the contributions of the model parameters estimated through ARD.
Accepted Version Manuscript
(Published Version: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compstruc.2023.107014)1. Introduction
Structural performance evaluation requires reliability analysis wherein the limit state capacity is statistically derived. It is useful to evaluate the performances of existing structures by considering the actual structure conditions to develop maintenance plans or implement reinforcement/retrofit activities in disaster events. Statistical performance analysis requires the consideration of the uncertainties of the structural properties using Monte Carlo (MC) calculations. The MC calculations require several to ten thousands of numerical calculations with a random sampling of the input parameter space. In modeling an existing structure with deteriorations or damages, a detailed model is required to represent the damage to the structural member; therefore, the number of model parameters becomes large. Moreover, the properties to consider the uncertainties due to the deterioration or damage should be included in addition to the uncertainties of the nominal model properties. In the case of performance evaluation under a disaster load such as an earthquake load, the MC calculations of multiple input load cases should be combined to consider the input load uncertainty. Therefore, high calculation effort is required to assess the structural performance.The surrogate model is a regression model that alternates the numerical analysis constructed using training data created through design of experiments (DoE) sampling of uncertain input parameters. The total cost of MC calculation can be reduced if a small amount of training data can appropriately represent the input–output relationship of the target numerical analysis. Numerous studies have been conducted on the application of the surrogate model to structural reliability analysis. The first application of surrogate model for the structural reliability analysis was shown by Bucher and Bourgund [1], where the performance function was approximated by the response surface method (RSM). The RSM has then been improved in many approaches, e.g., in studies by Kim et al. [2] and Zhao et al. [3]. Recently, support vector machine [4,5], polynomial chaos expansion [6,7], and artificial neural network (ANN) [8–10] are often adopted for surrogate modeling, and their effectiveness has been demonstrated. For instance, Marelli and Sudret [7] showed that the polynomial chaos expansion with active learning could construct surrogate models for structural analysis at low computational cost. The applicability of Gaussian process regression (GPR) to surrogate modeling has often been validated [11–14]. GPR [15] is a nonparametric regression method and does not require the determination of the model configuration; moreover, the number of hyperparameters required for the estimation is small, and it can be applied to nonlinear input–output relationships. For instance, Su et al. [12] conducted surrogate modeling by using GPR for the reliability analysis of bridges through finite element (FE) analysis. It was shown to be more efficient and accurate than the polynomial function-based response surface method. Avendaño et al. [14] constructed a GPR surrogate model that effectively predicts wind turbine loads with accuracy of 4% error or less. Adaptive learning method for GPR [16–22] have also been studied for efficient surrogate modeling of the structural reliability analysis, as surveyed by Moustapha et al. [23]. Adaptive learning is the method of incorporating additional learning points into the training data by evaluating the learning function. Some studies, e.g., EGRA by Bichon et al. [16] and AK-MCS by Echard et al. [17], successfully reduced the computational cost of surrogate modeling by implement adaptive sampling to the GPR. Since the AK-MCS was presented, Adaptive Kriging has been studied actively, e.g., AK-IS by Echard et al. [21] and AK-SS by Huang et al. [22]. Many studies on surrogate modeling have been conducted, although most of them can be applied only to target calculations. However, evaluations through numerical calculations to support decision-making in the engineering field require many similar calculations. The use of the surrogate model in such scenarios will require new training data for the same modeling procedure for each calculation. In other words, a surrogate model and its outputs cannot be used to construct other surrogate models.
Transfer learning (TL) is a machine learning technique in which the knowledge learned in a problem is utilized in the target problem [24]. TL is expected to be applicable to the surrogate modeling of a target numerical calculation that shows any similarity to the source numerical calculation for which a surrogate model is already available; this approach may reduce the computational costs of constructing new surrogate models. Some cases require the repetition of numerical calculations for evaluations in the civil structural engineering field. For instance, when the target calculation is the performance analysis of an existing structure with damages, the surrogate model of the numerical calculation for the initial undamaged condition is expected to be used as the source in the TL. The other is the seismic performance analysis of a structure considering various input earthquake loads. Once a surrogate model for an input earthquake load is constructed, it can be used to construct the surrogate models for other earthquake loads with similar characteristics. If the TL works effectively in these cases, the total computational cost of the structural performance evaluation is expected to be reduced.
Some previous studies have used TL in surrogate modeling. Xiong et al. applied TL to the deep learning model for the thermal analysis of spacecraft [25]. Kaya and Hajimirza applied ANN with TL to the optimization problem of thin-film multilayer solar cells [26]. Tian et al. used TL to construct the variable-fidelity surrogate model with a deep neural network for the buckling analysis of a composite shell with seven design variables and a hierarchical reinforced shell with nine design variables [27]. In all verifications, the prediction errors of the constructed surrogate models that used TL were significantly reduced. However, the studies [25–27] in which TL was used for the surrogate model assumed that the source and target data in TL are similar from the beginning of the process. In TL, the negative transfer problem is known to occur in some cases. Negative transfer refers to the issue wherein the performance of a machine learning model decreases owing to TL when the similarity between the source and target data, i.e., the input–output relationships between the source and target numerical calculations, is low [24]. For the use of TL with confidence, the possibility of this negative transfer must be considered when it is generally unknown whether the source and target numerical calculations are similar to each other.
In the engineering field, it is generally required to explain the results of physics numerical calculations for their appropriate use, i.e., provide explanations for the results from the viewpoint of validity of the modeling; this requirement applies to surrogate models as well. The issue in most machine learning techniques, which are applicable to surrogate modeling, is that the training and prediction process is a black box. In the structural performance analysis using surrogate models, it is essential to know which uncertainties of the structural properties contribute significantly to the demand output to provide the explainability of the surrogate model. A previous study mentioned the necessity of demonstrating the explainability of the surrogate model. Golparvar et al. [28] constructed a surrogate model for predicting the offshore wind power using GPR with an automatic relevance determination (ARD) kernel, which can estimate the contributions to the input parameters by the hyperparameters in the ARD kernel. The ARD kernel [29,30] is the kernel function to represent the correlation function in the Gaussian process (GP) model, which can assign different weights to each input dimension, and the corresponding length-scale is larger for input dimensions that are irrelevant to the output. Wipf and Nagarajan [30] showed that ARD can be applied to the linear model estimation problem, where the inputs are sparse relative to the output, while retaining the estimation accuracy. Owing to this feature, it is expected that the construction of GPR surrogate models with an ARD kernel can estimate the parameter contribution to the output. However, very few studies have provided the explainability of the use of a machine learning technique to surrogate modeling, especially in the structural engineering field. Furthermore, no study has considered both TL and explainability in surrogate models.
This paper develops surrogate modeling using GPR with TL (TL-GPRSM). GPR is also applicable to the surrogate modeling of structural performance analysis, because it can deal with nonlinear input–output relationships that may possibly emerge in the required structural analysis. In addition, as GPR is a nonparametric method, the number of model parameters to be determined can be relatively low when compared with that of other regression methods. Here, TL reduces the computational cost of surrogate modeling for structural performance analysis by considering the similarity in the input–output relationships in the numerical analysis. We also propose the use of the ARD kernel for providing the explainability of the constructed surrogate model and confidence assurance of TL. The appropriately estimated ARD kernel hyperparameters are expected to be useful in evaluating the degree of the TL effect in each target surrogate modeling and solving the issue of negative transfer.
In this paper, the overviews of GPR and TL are presented, and the TL-GPRSM is formulated. Then, two case studies are conducted to demonstrate the effectiveness of TL-GPRSM. The first is the live-load performance evaluation analysis of a steel plate girder bridge. Here, the target domain is the maximum stress evaluation of the bridge with corrosion damages, and the source domain is that of the bridge in the initial undamaged condition. The second case study is on the seismic performance evaluation of a seismic isolation bridge pier that requires nonlinear time-history analysis. Here, the target domain is the maximum displacement evaluation of the bridge pier and rubber bearing with the input as the recorded earthquake ground motion, and the source domain contains the inputs of ground motions provided in the design standard. The effectiveness of the TL-GPRSM is verified based on the accuracy of the constructed surrogate models and effect of computational cost reductions. In addition, the contribution of TL is discussed using the similarity evaluation based on ARD. Further, the contributions of uncertain parameters estimated through ARD to the output are validated using structural engineering observations.
2. Transfer training in GPR surrogate modeling
2.1 GPR with ARD kernel
GPR [15] is a nonparametric regression method and applicable to various input–output relationships. First, suppose an input-and-output data matrix $\mathbf{D}$ with number of data $N$ is defined as shown below. $$ \mathbf{D}=\{(\mathbf{x}_1,y_1),(\mathbf{x}_2,y_2),...,(\mathbf{x}_N,y_N)\}^T, $$ where $\mathbf{x}$ is a vector of the input parameters with length of $L$, and $y$ is the output. The input–output relationship is described as $$ y=f(\mathbf{x}). $$ Suppose that $y$ is standardized to the zero-mean variable, and $f$ is supposed to be generated from the following GP with zero mean. $$ f\sim\mathrm{GP}\big(\mathbf{0},k(\mathbf{x},\mathbf{x}^{\prime})\big). $$ Here, $\mathrm{GP}$ represents the Gaussian process and $k$ is a kernel function used to calculate the kernel matrix $\mathbf{K}$, which has $N$ rows and $N$ columns. $$ K_{nm}=k(\mathbf{x}_{n},\mathbf{x}_{m}), $$ where $K_{nm}$ is the element of $\mathbf{K}$ with $n$ rows and $m$ columns. Because $f$ in Eq. (2) follows the $\mathrm{GP}$, as shown in Eq. (3), the output vector $\mathbf{y}=(y_1,y_2,…,y_N )^T$ also follows the Gaussian distribution with zero mean and covariance matrix $\mathbf{K}$. $$ \mathbf{y}\sim\mathcal{N}(\mathbf{0},\mathbf{K}). $$ In this paper, we used the autoregressive relevance determination (ARD) kernel function [29]. In the ARD, the input parameters that contribute to the output can be determined automatically. Further, the performance of regression in GPR depends on the selection of the kernel function. For instance, if the Matern5/2 kernel is selected, ARD is applied as $$ k(r,\mathbf{\theta})=\sigma^2\left(1+\sqrt{5}r+\frac{5}{3}r^2\right)\exp(-\sqrt{5}r), \mathrm{where}\space r(\mathbf{x}_n,\mathbf{x}_m)=\sqrt{\sum_{i=1}^L\frac{(x_{ni}-x_{mi})^2}{l_i^2}}. $$ Here, $L$ is the number of dimensions of the input parameter vector, and $\mathbf{\theta}$ is a vector of the hyperparameters $\sigma$ and $l_i$. Among these hyperparameters, $l_i$ is called the length-scale, which indicates the contribution of the input parameter $x_i$ in the ARD. The smaller the estimation of the length-scale $l_i$, the larger is the contribution of $x_i$ to the output $y$. The estimator of GPR with ARD is thus the hyperparameter $\mathbf{\theta}$, which includes the length-scale $l_i$. To verify the contribution of each parameter, index $c_i$ was defined, which was the index converted from the length-scale $l_i$ to the relative percentage contribution in each input dimension $i$, as below. $$ c_i=\frac{1/l_i}{\sum_{j=1}^L(1/l_j)}\times100\quad(i=1,2,\cdots,L) $$ In this study, the maximum likelihood estimation was used for estimating the hyperparameters of GPR model $\mathbf{\theta}$ by adopting the limited-memory Broyden–Fletcher–Goldfarb–Shanno (L-BFGS) method [31] as the optimization method. The GPR model construction was implemented using the Python library GPy [32].2.2 TL in TL-GPRSM
TL in TL-GPRSM is implemented by the data expansion proposed by Daumé [33]. This method can apply to TL in most machine learning models including GPR by expanding the matrix of input parameters in training data to the common, source, and target parts. This makes possible to implement TL without losing advantages of GPR, applicability to nonlinear and nonparametric regressions. Furthermore, as the ARD kernel can be applied straightforward, the explainability of constructed TL-GPRSM is introduced including the effectiveness of TL.The input–output relationship of the target numerical analysis for surrogate modeling is called the “target domain.” The “source domain” is the input–output relationship of the previously trained model. For successful TL, the input–output relationship of the source domain is required to be similar to that of the target domain. First, suppose that the source domain data $\mathbf{D}^s$ and target domain data $\mathbf{D}^t$ are described as $$ \mathbf{D}^s=\left\{(\mathbf{x}_1^s,y_1^s),(\mathbf{x}_2^s,y_2^s),...,(\mathbf{x}_{N_s}^s,y_{N_s}^s)\right\}, $$ $$ \mathbf{D}^t=\left\{(\mathbf{x}_1^t,y_1^t),(\mathbf{x}_2^t,y_2^t),...,(\mathbf{x}_{N_t}^t,y_{N_t}^t)\right\}, $$ where the vector $\mathbf{x}$ is the input variables vector and $y$ is output value. The number of data in the source domain is $N_s$ and that in the target domain is $N_t$. The data expansion for TL is implemented by configuring the expanded input vectors for the target domain $\hat{\mathbf{x}}^{t}$ and source domain $\hat{\mathbf{x}}^{s}$ using input vectors $\mathbf{x}^s$ and $\mathbf{x}^t$, respectively, as follows: $$\hat{\mathbf{x}}^s=(\mathbf{x}^s,\mathbf{x}^s,\mathbf{0}) \mathrm{and}\quad\hat{\mathbf{x}}^t=(\mathbf{x}^t,\mathbf{0},\mathbf{x}^t).$$ The expanded input and output data $\mathbf{D}^{TL-GPRSM}$ for TL-GPRSM are as follows: $$\mathbf{D}^{TL-GPRSM}=\left\{(\mathbf{\hat{x}}_{1}^{s},y_{1}^{s}),(\mathbf{\hat{x}}_{2}^{s},y_{2}^{s}),...,(\mathbf{\hat{x}}_{{N_{s}}}^{s},y_{{N_{s}}}^{s}),(\mathbf{\hat{x}}_{1}^{t},y_{1}^{t}),(\mathbf{\hat{x}}_{2}^{t},y_{2}^{t}),...,\left(\mathbf{\hat{x}}_{{N_{T}}}^{t},y_{{N_{T}}}^{t}\right)\right\}^{T}.$$ TL can be realized by constructing a GPR model using the data matrix in Eq. (11) as training data. The objective of this formulation is to expand the input vector $\mathbf{x}$ to three parts: “common part,” “source part,” and “target part,” as shown in Fig. 1. TL-GPRSM is then realized by constructing a GPR model using these expanded data. This means that the information of the source domain is used in training the target domain model. Within the expanded input and output data, the common part considers both the source and target domains, the source part considers only the source domain, and the target part considers only the target domain. The contribution of each part to the constructed GPR model indicates the utility of the TL. By adopting the ARD kernel for GPR, it becomes possible to derive the contribution of each part. Here, the contribution of each input dimension can also be derived using Eq. (7). The contribution for each part can be calculated by adding the contribution ci, where i indicates the component corresponding to each part. $$ C_C=\sum_{i=1}^{L_C}c_i,\space C_S=\sum_{i=1}^{L_S}c_i,\space \mathrm{and} C_T=\sum_{i=1}^{L_T}c_i. $$ Here, $C_C$, $C_S$, and $C_T$ are the contributions of the common, source, and target parts, and $L_C$, $L_S$, and $L_T$ are the number of input dimensions of the common, source, and target parts, respectively. Considering that the common part contributes to both the source and target domains, the relative magnitude of $C_C$ against $C_T$ indicates the effect of TL in predicting in the target domain.

2.3 Construction and validation of TL-GPRSM
In the construction of TL-GPRSM developed in this paper, the training and test datasets for the source and target domains are created through numerical calculations of the structural model with the input parameter sets generated by Latin hypercube sampling (LHS) [34]. The hyperparameters of GPR are then estimated using L-BFGS optimization.The performance of constructed surrogate model was evaluated by the prediction error with respect to the test data and the accuracy of predicted probability distribution of output, which is required for the structural reliability analysis. It is particularly important for the surrogate modeling for structural reliability analysis to be able to predict the appropriate distribution of output response. The root means square percent error (RMSPE) was used for the evaluation of the prediction error. The agreement of distributions was evaluated using not only the overlay of cumulative distributions but also the p-value in the Kolmogorov–Smirnov (KS) test. In each verification case, the surrogate model was constructed for the ten training datasets created through ten trials of LHS sampling, and the variations in the accuracy and probability distributions were derived for evaluating the modeling stability.
The computational cost of surrogate modeling was evaluated by the required number of times of numerical calculations of the structural model (e.g., FE model) to predict the accurate distribution of output response. Here, it should be noted that the computational cost of prediction using constructed surrogate model is negligible compared to the computational cost of numerical analysis of the structural model. The TL-GPRSM is expected to realize reducing the number of training data in the target domain by taking advantage of data in the source domain, which has been already existed.
The explainability of the constructed surrogate model and confidence assurance of the TL were then evaluated based on the percentage contributions derived using the estimated length-scales in the ARD kernel. Structural reliability analysis is the procedure of considering the uncertainties of multiple parameters for evaluating the limit state capacity. However, the number of parameters contributing to the output required for the performance evaluation is actually limited in many cases. This sparsity of the contribution can be estimated by using the ARD kernel. The contribution of each input dimension $c_i$, derived using Eq. (7) with the estimated length-scale $l_i$, indicates the extent to which the uncertainty of the corresponding model parameter affects the demand output. The constructed surrogate model can be accepted when the contributing model parameters can explain the structural response output behaviors from the viewpoint of the physics of the structure. Furthermore, the contributions of the common, source, and target parts, which are the summed contributions of the dimensions belonging to each part, calculated using Eq. (12), is used for evaluating the effectiveness of TL. Here, TL is considered effective when the contribution of the common part $C_c$ against $C_T$ is relatively high.
2.3 Application example of TL-GPRSM
A simple application example is shown to recognize the significance of TL-GPRSM. Here, the function models, $f_s$ and $f_t$, are given as the source domain and the target domain, respectively. $$f_s(\mathbf{x})=2{x_1}^2+{x_2}^2+0.00001x_3+5$$ $$f_t(\mathbf{x})=2x_1^2-2(x_2-1)\sin x_2+0.00001x_3+5$$ where $x_1$, $x_2$, and $x_3$ are input variables with the range of $−1≤ x_i ≤1 (i =1−3)$, and the input vector is configured as $\mathbf{x}=(x_1, x_2, x_3)$. Seeing the similarity between those two function models, only the terms of $x_2$ acts on the output differences between the models of source domain $f_s$ and target domain $f_t$, and contributions of the terms of $x_1$ and $x_3$ and the constant terms are the same in both models. In addition, the coefficient of each term indicates how much that term contributes to the output of function. It is obvious that coefficients on $x_3$ are relatively small in both models.First, the data sets of function input-output relationships for source domain $f_s$ and target domain $f_t$ are created with the numbers of data $N_s =100$ and $N_t =10$, respectively. The samples of input variables space are plotted in Fig.2, where they are shown in the spaces of $x_1$ and $x_2$ because $x_3$ less contributes to the function output, as mentioned above. The data matrix of source domain $\mathbf{D}^s$ and target domain $\mathbf{D}^t$ are represented as: $$\mathbf{D}^s=\{\left(\mathbf{x}_1^s,f_s(\mathbf{x}_1^s)\right),\left(\mathbf{x}_2^s,f_s(\mathbf{x}_2^s)\right),...,\left(\mathbf{x}_{100}^s,f_s(\mathbf{x}_{100}^s)\right)\}^T.$$ $$\mathbf D^t=\{\bigl(\mathbf x_1^t,f_t(\mathbf x_1^t)\bigr),\bigl(\mathbf x_2^t,f_t(\mathbf x_2^t)\bigr),...,\bigl(\mathbf x_{10}^t,f_t(\mathbf x_{10}^t)\bigr)\}^T,$$
 |  |
Then, the expanded input vectors for implementing TL are configured following Eq. (10), as: $$\hat{\mathbf{x}}_i^s=(\mathbf{x}_i^s,\mathbf{x}_i^s,\mathbf{0}_{\mathbf{1}\times\mathbf{3}})(i=1-100) \space \mathrm{and} \space \hat{\mathbf{x}}_j^t=(\mathbf{x}_j^t,\mathbf{0}_{\mathbf{1}\times\mathbf{3}},\mathbf{x}_j^t) (j=1-10).$$ The data matrix for TL-GPRSM is given as follows: $$\mathbf{D}^{TL-GPRSM}=\{\left(\mathbf{\hat{x}}^{s}{}_{1},f_{s}(\mathbf{x}_{1}^{s})\right),\left(\mathbf{\hat{x}}^{s}{}_{2},f_{s}(\mathbf{x}_{2}^{s})\right),...,\left(\mathbf{\hat{x}}^{s}{}_{100},f_{s}(\mathbf{x}_{100}^{s})\right),\ \left(\mathbf{\hat{x}}^{t}{}_{1},f_{t}(\mathbf{x}_{1}^{t})\right),\left(\mathbf{\hat{x}}^{t}{}_{2},f_{t}(\mathbf{x}_{2}^{t})\right),...,\left(\mathbf{\hat{x}}^{t}{}_{10},f_{t}(\mathbf{x}_{10}^{t})\right)\}^{T}$$ The obtained surrogate model for target domain $f_t$ is then evaluated by predicting the distribution of function outputs to 1000 samples generated from the space of input variables $x_i$ with range of $−1≤ x_i ≤1 (i =1−3)$. For comparison, a GPR surrogate model without TL is also constructed only using the 10 data from the target function model ft. The predicted distributions are compared in Fig.3 (a). Here, the distribution of function outputs created by assigning the same 1000 samples of input variables to the target function model $f_t$ is also shown as “True” case. The TL-GPRSM can predict the distribution closer to the true distribution than the one predicted from the GPR model without TL. The RMSPE accuracies are 0.13% and 15.2% in TL-GPRSM and GPR without TL, respectively. Also, the function field of ft predicted by the TL-GPRSM in Fig. 3(b) clearly shows good agreement with the true function field, which is shown in Fig. 2(b), compared to the function field predicted by the GPR without TL in Fig. 3(c).
The contribution of each input variable in each of Common, Source, and Target parts is then evaluated by calculating $c_j$ using Eq. (7) as: $$c_j=\frac{1/l_j}{\sum_{j=1}^9\left(1/l_j\right)}\times100\quad(j=1,\cdots,9),$$ where $l_j$ is length-scale in ARD kernel, and subscript $j$ indicates the order of each input parameter in expansion data, i.e., $j=1−3$ indicates three input variables $x_1-x_3$ in “Common” part, $j=4−6$ indicates those in “Source” part, and $j=7−9$ are those in “Target” part. Those parts correspond to the “Common”, “Source”, and “Target” parts presented in Fig.1. Figure 4 shows calculated contribution index $c_j$. In the “Common” part, only input variable $x_1$ has non-zero value. This indicates that the terms of $x_1$ contribute similarly to both function outputs of the source domain fs and the target domain $f_t$. On the other hand, there is no contribution in $x_2$ in “Common” part, and the term of $x_2$ shows significant contribution in each of “Source” and “Target” parts. These points are understandable because the terms of $x_1$ are the same in the two function models, $f_s$ and $f_t$, and the terms of $x_2$ are different between them, as shown in Eqs. (13) and (14). In addition, almost zero values in x3 in all parts indicate consistency with the point that the terms of $x_3$ have small coefficients in both model functions. The effect of TL can be determined by the summation of contribution $c_j$ in each part, which are $C_C$, $C_S$, and $C_T$ expressed in Eq. (12). The calculated values of $C_C$, $C_S$, and $C_T$ are 39.5, 27.1 and 33.4, respectively. It can be said that the TL worked effectively for the appropriate surrogate modeling from the point that the relative value of common part contribution $C_C$ against target part contribution $C_T$ was large in this application example.
 | |
 |  |

(Left: Common part, Center: Source part, Right: Target part)
3. Live-load capacity evaluation of plate girder bridge
TL-GPRSM is expected to be applicable to the case wherein the number of input parameters and their uncertainties change in the source and target domains of the TL. In existing structures, the number of uncertain parameters and their degrees of uncertainties may change from those at the time of new construction owing to damage or deterioration. In this case, if TL-GPRSM is effective, the computational cost of the reliability analysis can be reduced by using the data saved in the design phase. In this section, we use the analytical model of a steel plate girder bridge with damaged sections. The surrogate model was constructed by applying TL-GPRSM to the data before and after the damage, and its effectiveness in reducing the computational cost was verified. The effectiveness of TL and adaptation to the sparsity of input parameters using ARD contribution estimation were also verified.3.1 FE modeling and evaluation analysis
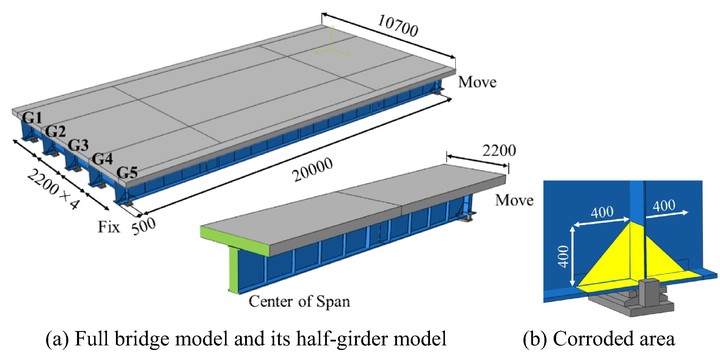
The numerical analysis as the target of surrogate modeling in this paper was the structural reliability analysis of a simply supported steel plate girder bridge considering the damage of corrosion at the end of the main girder, which was conducted in a previous study by the authors [35]. The bridge is a testbed structure for the numerical study designed based on the Japanese design standard [36]. The bridge consists of five main I-shape steel girders, a reinforced concrete (RC) slab, and steel bearings with a span length of 20.0 m and width of 10.7 m. The FE model of the bridge was constructed using the general-purpose FE analysis software Abaqus 6.14. Figure 5(a) shows the overall view of the constructed whole-bridge FE model. Here, the five main girders and concrete slab were modeled using the shell element, and the members of the steel bearings were described using the solid element. The output response for the performance evaluation was the maximum Mises stress at the region near the ends of each main girder under static loading of the designed live load introduced in the Japanese design standard [36]. The convergence of the mesh size to the output response was verified to determine the mesh size configuration for the whole-bridge model; however, the determined number of elements became excessively large. Therefore, the half-girder model was prepared to reduce the computational cost, as shown in Fig. 5(a). Here, the previously determined mesh configuration was retained, and the continuity condition at the mid-span cross-section was applied with symmetry preservation. In addition, the input live load was adjusted to obtain the stress distribution at the main girder as the output, which was consistent with that obtained in the whole-bridge model analysis. The total number of elements in the half-girder model was 104,799. Most parameters of the initial model without damages were determined based on the nominal properties of steel and RC used in the bridge design. The friction coefficient of the contact surface between the upper and lower parts of the steel bearing was set to 0.2, which is the generally used value of the coefficient for metal contact surfaces. In the constructed initial FE model, the static deflection under the designed live load satisfied the requirement for the limit state in the design standard [36]. Then, the FE model for the performance evaluation under the damaged condition was constructed. The corrosion at the main girders and bearings was represented by setting the individual areas in the main girders, as shown in Fig. 5(b), to reduce the thickness at the corroded areas and by increasing the friction coefficients at the corroded bearings, respectively. The effect of cracks at the concrete slab was considered by reducing the Young’s modulus of the elements of the slab. The input–output relationship of the initial FE model is the source domain, and that of the FE model with damages is the target domain in the TL-GPRSM. |  |
3.2 Uncertainties of model parameters
In the TL-GPRSM, the increase in the uncertainties in the structural properties due to damages is considered through TL. The parameter uncertainties were determined both in the initial FE model as the source model and in the damaged-condition FE model as the target model. In the initial FE model, sixteen parameters #1–#16 were considered, and their uncertainties were represented by the uniform distributions with nominal mean and coefficient of variation (COV), as shown in Table 1. Here, the mean and COV values were determined based on the statistical properties reported in previous research papers and surveys, as summarized in the authors’ previous study [35]. For the damaged-condition FE model, three parameters #17–#19 were added to represent the effect of corrosion, that is, the thickness reduction at the corroded areas. In addition, the probability distribution of the friction coefficient #8 (Cf) was changed to represent the decrease in the moving function due to the corrosion, and the distribution of the Young’s modulus of the concrete slab #3 (Ec) was changed to consider the effect of cracks.Figure 6 shows the distributions of the maximum Mises stress near the ends of the girders for the performance evaluation using MC calculations with 500 samples from the space of uncertain model parameters in the initial- and damaged-condition FE models. Here, the 500 samples were generated through LHS. The maximum Mises stress in the damaged-condition FE model is distributed in the range of higher stress values when compared with the distribution in the initial FE model. It can be said that the limit state capacity of yield stress is reduced owing to the damages. The distribution of the maximum Mises stress in the damaged-condition FE model is the target output of the surrogate modeling using the TL-GPRSM. The surrogate model for the initial FE model with sixteen uncertain model parameters as the inputs is the source domain, and that for the damaged-condition FE model with nineteen parameters as the inputs is the target domain. Although the number of input parameters is different between the source and target domains, the TL-GPRSM is applied by data expansion with 16 dimensions for the common part, 16 dimensions for the source part, and 19 dimensions for the target part.
| FE model parameter (Unit) | Initial (Source) | Damaged (Target) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nominal | COV | Nominal | COV | |||
| #1 | $D_c$ | Density of concrete slab (kg/m³) | 2400 | 0.0171 | * | * |
| #2 | $E_s$ | Young's modulus of steel main girders (GPa) | 200 | 0.0450 | * | * |
| #3 | $E_c$ | Young's modulus of concrete slab (GPa) | 25 | 0.0167 | 22.5 | 0.0333 |
| #4 | $E_b$ | Young's modulus of steel bearings (GPa) | 200 | 0.0450 | * | * |
| #5 | $V_s$ | Poisson's ratio of steel main girder | 0.3 | 0.0910 | * | * |
| #6 | $V_c$ | Poisson's ratio of concrete slab | 0.2 | 0.0167 | * | * |
| #7 | $V_b$ | Poisson's ratio of steel bearing | 0.3 | 0.0910 | * | * |
| #8 | $C_f$ | Friction coefficient of steel bearing | 0.2 | 0.0167 | 0.9 | 0.0333 |
| #9 | $T_{uf1}$ | Thickness of upper flange of steel girder at near-end section (m) | 0.0190 | 0.0121 | * | * |
| #10 | $T_{uf2}$ | Thickness of upper flange of steel girder at mid-span section (m) | 0.0300 | 0.0121 | * | * |
| #11 | $T_w$ | Thickness of web plate of steel girder (m) | 0.0090 | 0.0121 | * | * |
| #12 | $T_{lf1}$ | Thickness of lower flange of steel girder at near-end section (m) | 0.0270 | 0.0121 | * | * |
| #13 | $T_{lf2}$ | Thickness of lower flange of steel girder at mid-span section (m) | 0.0300 | 0.0121 | * | * |
| #14 | $T_{st1}$ | Thickness of stiffener of steel girder at near-end section (m) | 0.0130 | 0.0121 | * | * |
| #15 | $T_{st2}$ | Thickness of stiffener of steel girder at mid-span section (m) | 0.0100 | 0.0121 | * | * |
| #16 | $T_{stn}$ | Thickness of stiffener of steel girder at other sections (m) | 0.0065 | 0.0121 | * | * |
| #17 | $T_{lf-d}$ | Thickness of corroded area in lower flange of steel girder at near-end section (m) | − | − | 0.025 | 0.0270 |
| #18 | $T_{w-d}$ | Thickness of corroded area in web plate of steel girder (m) | − | − | 0.008 | 0.0162 |
| #19 | $T_{st-d}$ | Thickness of corroded area in stiffener of steel girder at near-end section (m) | − | − | 0.012 | 0.0162 |

3.3 TL for FE model analysis in damaged condition
The training dataset in the source domain was configured using the sampled 16-dimension uncertain model parameter sets and their output responses, i.e., the maximum Mises stress near the end of the girder, in the initial FE model. The dataset in the target domain comprised the inputs sampled from the space of 19-dimension uncertain parameters and their output responses in the damaged-condition FE model. The TL-GPRSM was constructed using the input-output data from the FE analysis in the initial condition as the source domain and the input-output data from the FE analysis in the damaged condition as the target domain.In the verification, a fundamental dataset that consists of 500 input–output relationships was prepared by conducting FE analysis for 500 input model parameter samples to configure the training and test datasets in the target domain. For $N$ number of training data, $N$ input–output relationships were randomly selected from the fundamental dataset, and the remaining were used as the test data. The accuracy of the surrogate model was verified using the RMSPE. The p-value of the KS test was also derived to evaluate the agreement between the maximum Mises stress distributions from the surrogate model and those from the MC calculation using the FE model. In each case, surrogate modeling was performed for ten training datasets for evaluating the modeling stability.
The number of training data in the source domain, i.e., the initial FE model, was varied to evaluate how it affected the accuracy of the TL-GPRSM by setting the cases of 10, 30, and 100 source domain data. The average of RMSPEs for ten GPR surrogate models for the initial FE model in each case was 3.1 in the case of 10 data, 0.10 for 30 data, and 0.0096 for 100 data. It is known that the accuracy of regression increases with the amount of data. The target surrogate model constructed using the TL-GPRSM was then verified. The RMSPE of the constructed surrogate model for the damaged-condition FE model is shown in Fig. 7. Here, the horizontal axis is the number of training data in the target domain. The red line is the accuracy obtained by the TL-GPRSM, and blue line is the result obtained using only the data from the damaged-state FE model. The average and variance of ten surrogate models constructed by ten times samplings were plotted. For each number of source domain data, the RMSPE in the TL-GPRSM converged to a low value faster than that of the surrogate model constructed using only the data from the damage-condition FE model. This indicates that the use of TL-GPRSM can reduce the number of numerical calculations of the damage-condition FE model if there are numerical results from the initial FE model. As the number of source data increases, the RMSPE value and its variation become smaller, i.e., the accuracy and stability of surrogate modeling improve. For all numbers of source domain training data, a surrogate model with accuracy of less than 1% can be obtained by using 15 training data in the target domain. For instance, considering the total computational cost, the accuracy of the surrogate model with 1% RMSPE can be achieved by using 10 source data and 15 target domain data in the TL-GPRSM. Although this accuracy can be obtained by the target-only surrogate model using 25 training data from the damaged-condition FE model, TL-GPRSM ensures higher stability.
The distributions of the maximum Mises stress derived from the constructed surrogate models are depicted in Fig. 8(a). The red lines denote the cumulative distributions of the maximum Mises stress predicted from the surrogate models constructed by the TL-GPRSM using 30 source data and 15 target data. The distributions obtained by ten TL-GPRSMs show good agreement with the distribution obtained by the MC calculation of the FE model, which is shown as a black solid line. The blue lines are the distributions derived through GPR using only the 15 target domain data, which do not agree with the distribution obtained with the FE model MC calculation. Hence, the prediction stability of TL-GPRSM is much higher than that in the case of GPR modeling using only 15 target domain data. In addition, the average of R2 index, which is to evaluate regression performance, over ten trials, was 0.98 in TL-GPRSM; on the other hand, that in GPR surrogate model without TL was 0.57. The R2 index also indicates that the TL-GPRSM realized more accurate surrogate modeling. The plots of the p-values in the KS test are also shown in Fig. 8(b). The high p-value indicates that the similarity between the two distributions corresponding to the surrogate model and FE model is high. As the number of target domain training data increases, the p-value in the TL-GPRSM reaches a high value faster than that in the case of the GPR model using only the target domain data. It can be concluded that high accuracy and high stability can be obtained using the surrogate model constructed with the TL-GPRSM.
Figure 9 shows plots of $C_C$, $C_S$, and $C_T$ expressed in Eq. (12) against the number of target domain training data to evaluate the effect of TL. In each plot, the red line shows the relative value of the length-scale sum of the common part, and the blue and green lines show those of the target part and source part, respectively. Each plot represents the ten-time average for each number of target data. In these plots, the higher the value of the common part when compared with that of the target part, the greater is the effect of the TL. In Fig. 9 (a)-(c), the contribution values of all parts are almost converged for the number of target domain data of 10–15 in all cases of the source domain data. Moreover, the effect of TL increases as the number of source domain data increases. The significance of TL is enhanced when a larger number of training data is used in the source domain.
Figure 10 shows the contribution of each uncertain model parameter in the constructed surrogate model, that is, the relative value of the inverse length-scale estimated in the TL-GPRSM with 30 source domain data and 15 target domain data. The results are shown separately for the expanded data vector's common, source, and target parts. First, the friction coefficient at the bearings, $C_f$, shows the highest contribution in the common part. This is interpreted as the similarity in the contribution of parameter $C_f$ to the output in the target and source domains. It can also be seen that the contributions of these parameters are sparse, i.e., some parameters show little contribution; therefore, the significant parameters in the input–output relationship of the target surrogate model can be extracted from this figure. In the initial state analysis of the source domain, the parameters contributed significantly to the overall bending behavior. Regarding parameters with high contributions, the contribution of the steel girder web thickness $T_w$, which is related to the overall bending stiffness of the girder, was significant. The parameters $T_{bf1}$, $T_{stc}$, and $E_b$ representing the characteristics near the girder ends, which are correlated with the boundary conditions, also had an effect. This result is reasonable based on structural engineering findings. However, in the source domain, which is the damaged-state analysis, the contribution was large for parameters related to localized deterioration damage, such as lower flange thickness $T_{bf-d}$ and web thickness $T_{w-d}$ at the girder end corrosion area. These estimated contributions are consistent with the findings in structural engineering that the stress at the girder end increases as the corrosion loss progresses. The validity of these estimated contributions supports the explanatory power of the TL-GPRSM.









4. Performance evaluation of seismic isolated bridge pier
Another application of the structural reliability analysis is performance evaluation against disaster loads such as earthquakes. Here, the structural response analysis requires a nonlinear calculation, and must be performed for various external loads that are probabilistically determined. In this section, the TL-GPRSM was verified using the earthquake response analysis for the seismic performance evaluation of an isolated RC bridge pier. In this section, TL-GPRSM is constructed with the source domain as the input–output of seismic response analysis with the designed earthquake loads, and the target domain as the input–output of seismic response analysis for a certain input observed earthquake load. We verified whether the computational cost of the seismic performance analysis of the structure could be reduced by using the prepared data created based on numerical analysis with the designed earthquake loads.4.1 Modeling and parameter uncertainties
The numerical model of a seismic isolation RC pier used in this verification corresponds to the dynamic seismic design shown in the design standard of road bridges in Japan [37]. Figure 11(a) shows the overall view of the bridge, and the target is an RC pier with seismic rubber bearing, indicated as P1. This pier was modeled using the two degree-of-freedom (DOF) lumped-mass model shown in Fig. 11(b). The masses of the superstructure and RC pier were assigned to the upper and lower lumped-masses of the 2DOF system, respectively, and the seismic isolation rubber bearing was modeled as a horizontal spring with nonlinear characteristics described using the bilinear model. The nonlinear stiffness of the RC pier was described using the Takeda model [38]. The nominal parameters were determined based on the values of the bridge properties introduced in the design standard [37], as shown in Table 2. The uncertainty of each model parameter was represented as a uniform distribution with upper and lower limits of ±10% from the nominal value.

| Parameter | Nominal | Uncertainty | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Superstructure | Mass (Mu) | 604000 kg | ± 10 % |
| Seismic isolation bearing | Primary stiffness (Kb1) | 40023.2 kN/m | |
| Secondary stiffness (Kb2) | 6154.4 kN/m | ||
| Yield load (Qb) | 1117.2 kN | ||
| RC Pier | Mass (Mrc) | 346300 kg | |
| Primary stiffness (Krc1) | 110000 kN/m | ||
| Secondary stiffness (Krc2) | 8250 kN/m | ||
| Yield load (Qrc) | 3399 kN | ||
4.2 Input earthquake loads and nonlinear time-history analysis
The input earthquake loads for the target domain in the TL-GPRSM were the designed ground motion in the design standard [39] and two observed earthquake ground motions recorded as JMA Kobe for the Kobe earthquake in 1995 and KAIHOKUBASHI for the Tohoku earthquake in 2011, as shown in Table 3. As the source domain, the designed earthquake ground motion, called Level-2 ground motion, was adopted, which was used for evaluation based on the time-history analysis. Two types of Level-2 ground motions were considered, namely, Type-1 for the plate boundary type earthquake and Type-2 for the inland earthquake. In the design standard [39], three ground motions were prepared for each of Type-1, Type-2, and three ground classifications. Here, the seismic isolation bridge was allowed to be constructed on hard ground; hence, the earthquake ground motions for the corresponding ground classification were used: Type1-1-1/2/3 and Type2-1-1/2/3. For the source domain in all cases, the first ground motions of the two types, Type1-1-1 and Type2-1-1, were adopted. As shown in Table 3, the second ground motion of Type-2, Type2-1-2, was set for the target domain in Case #1. One of the purposes of this verification was to investigate how the similarity in the input earthquake ground motion affected the performance of the TL-GPRSM. It should be noted that JMA KOBE was classified as an inland earthquake (Type-2) and KAIHOKUBASHI as a plate boundary type earthquake (Type-1). The acceleration response spectra for all ground motions for the target and source domains are shown in Fig. 12. In Type-1 ground motion, high response was observed in the low-range period of less than 0.3 s, and the dominant period in Type-2 ranged from approximately 0.3 to 0.8 s. For the nonlinear time-history analysis, the time increment was set to 0.001 s, and the Newmark-β method (γ = 0.5 m, β = 0.25) was adopted for the numerical integration. The structural damping was assumed to be Rayleigh damping with the component damping coefficient of 0% for the seismic isolation bearing and 2% for the RC pier.Figure 13(a) and (b) show the response hysteresis of the RC pier and seismic rubber bearing obtained from the results of the time-history analysis for the input cases of JMA KOBE and KAIHOKUBASHI, respectively. Although both earthquake inputs had the same intensity level as the designed input earthquake for each earthquake type, and both showed the maximum displacements in the pier and bearing, the occurrences of nonlinearity were different. In Fig. 13 (a) for JMA KOBE, not only the rubber bearing but also the RC pier showed plasticized responses. However, the RC pier response was in the elastic range by utilizing the rubber bearing in Fig. 13(b) corresponding to KAIHOKUBASHI. It is well known that the nonlinear response of each member strongly depends on the input ground motion. The TL is expected to effectively consider the input–output relationship of each earthquake type trained in the source domain, in the target domain training.
| Case # | Target domain | Source domain |
|---|---|---|
| Case #1 | Level2 Type2-1-2 | Level2 Type1-1-1 (200 data) Level2 Type2-1-1 (200 data) |
| Case #2 | JMA KOBE (Type-2) | Level2 Type1-1-1 (200 data) Level2 Type2-1-1 (200 data) |
| Case #3 | KAIHOKUBASHI (Type-1) | Level2 Type1-1-1 (200 data) Level2 Type2-1-1 (200 data) |

 |  |
 |  |
4.3 Surrogate model construction using TL-GPRSM
Figures 14−16 show the accuracies and effects of TL in the constructed surrogate models in Cases #1−#3. In this verification, all surrogate models were constructed using 200 Type1-1-1 data and 200 Type2-1-1 data, with the data having a higher TL effect as the source domain data, as shown in Table 3. For setting the training and testing datasets in the target domain, a fundamental dataset was prepared by creating 10,000 input–output relationships of the nonlinear time-history analysis of the 2DOF lumped-mass model. In each figure, plot (a) depicts the comparison of the accuracies based on RMSPE between the surrogate models constructed using the TL-GPRSM and those constructed using GPR with only the target domain data, plotted against the number of target domain training data. Plot (b) shows the relative contributions of the common, source, and target parts, calculated from the estimated length-scales of ARD, and plot (c) depicts the comparison of the contributions of the common part for each of the two source domains: Type1-1-1 and Type2-1-1. In Case #1 with the target domain of Type2-1-2, the RMSPE of the TL-GPRSM is slightly lower than that of the surrogate model constructed using GPR in the range of number of target domain data smaller than 50; further, the accuracies in the cases with number of training data over 50 show little difference, as shown in Fig. 14(a). This means that the TL was not useful in ensuring effective surrogate modeling. From the plots in Fig. 14(b), the contribution of the common part to the target part was almost constant, ranging from 10 to 15%, beyond the number of training data of 10. Figure 14(c) shows that the contribution of Type2-1-1 was higher than that of Type1-1-1. This means that the output of the maximum displacement of the RC pier mainly considers the source domain of Type2-1-1, which is the same type of input ground motion as that of the target domain. However, the output of the rubber bearing mainly considers Type1-1-1. |  |
 |  |
 |  |
In Case #2 with the target domain of JMA KOBE, the surrogate models by TL-GPRSM show slightly higher accuracy for both the RC pier and isolation bearing, especially when approximately 30 target domain data are used, as shown in Fig. 15(a). Figure 15(b) shows that the relationship between the contributions of the common and target parts is constant, as seen in Case #1, and the ratios of those two contributions are similar. In Fig. 15(c), the contribution of the common part for each of the two source domains shows the same trend as that in Fig. 15(c), both for the RC pier and seismic isolation bearing; however, the difference between the contributions of Type1-1-1 and Type2-1-1 decreases.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
In the case of KAIHOKUBASHI in Fig. 16(a), the accuracy of the TL-GPRSM for the RC pier almost overlaps that of the surrogate model constructed using only the target domain training data. However, the accuracy of the TL-GPRSM for the bearing improves, especially when the number of training data is less than 100. Considering the range in Fig. 16(b), the contribution of the common part to the target part is relatively high. This indicates that the TL was effective in the surrogate model construction for the RC pier in this case. However, the RMSPE of the bearing surrogate model was approximately three times higher than those of all the other surrogate models, including those of the two previous cases. Figure 16(c) does not show a clear trend in which source domain data were selected in the TL for the surrogate model of the RC pier; however, for the bearing, there was a tendency to select the source domain of Type2-1-1, although the KAIHOKUBASHI ground motion is related to the plate boundary.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
Figure 17 shows the estimated contributions of each model parameter uncertainty to the demand output for discussing the explainability of the constructed surrogate models. Here, the contributions to the maximum displacement of the RC pier are shown in Case #2 and Case #3 in Fig. 17(a) and (b), respectively. Notice that highly nonlinear behavior occurred in Case #2 (JMA KOBE) but did not occur in Case #3 (KAIHOKUBASHI), as explained in Fig. 13. The plot of red bars shows the contributions of the model parameters in the common part, the one with green bars denotes those in the source part, and the plot of blue bars denotes the contributions in the target part. It can be first understood that no parameter significantly contributed to the output in the common part in both cases. This is considered the reason why the TL was not effective in these cases. The plot of the target part indicates how each model parameter is considered in each target surrogate model. It can be seen that the contributions of the parameters that are related to the nonlinear behavior, such as Kb2, Qb, and Qrc, are high in Case #2 (JRA KOBE), whereas the contribution of those parameters is much lower in Case #3 (KAHOKUBASHI). These show the consistencies in the structural responses, i.e., occurrences of nonlinearity, which depend on the input earthquake waveform. Even though the effect of TL in computational cost reduction was not achieved by the TL-GPRSM in the cases considered here, the validity of the constructed surrogate models could be assured by observing the estimated contributions. Further considerations of the surrogate modeling of nonlinear dynamic systems with effective TL are required in a future study.


However, the constructed surrogate models can provide appropriate distributions of the maximum displacements for seismic evaluation. Figure 18 shows the cumulative distributions of the maximum displacements of the RC pier and seismic isolation rubber bearing in Case #2. The surrogate model was constructed using TL-GPRSM with the number of target domain data as 50. Ten red lines denote the distributions from the ten surrogate models constructed by ten-time DoE samplings of the data. The black line denotes the distributions derived using the 2DOF model MC calculations with 10,000 samples. Especially in the RC pier, the distribution from the surrogate model shows good agreement with those from the MC calculation along with high stability. In the bearing, the both-side tails of the distributions from the surrogate models do not show high accuracy and stability.
 |  |
5. Conclusions
The GPR surrogate model with TL (TL-GPRSM) was proposed in this paper. The computational cost for constructing a surrogate model of the target analysis was reduced by using the data of the input–output relationships of the source analysis with any similarity to those of the target analysis. The use of the ARD kernel in GPR was suggested to evaluate the effectiveness of TL and explainability of the constructed surrogate model. Two case studies were conducted to verify the significance of TL-GPRSM. The conclusions are summarized as follows:
- TL-GPRSM was applied to the surrogate modeling of the live-load performance evaluation of a steel plate girder bridge with corrosion damage by applying the source analysis of the undamaged condition. The prediction error was less than 1% RMSPE when 15 target domain data were used. This is equivalent to the accuracy obtained with 25 target data for the surrogate model without TL, regardless of the number of source data.
- The predicted cumulative distribution of the maximum stress in the TL-GPRSM had less uncertainty and the shape was closer to that obtained with the numerical results than the surrogate model without TL using the same number of target data.
- The TL effect could be determined from the contribution of the common part calculated from the ARD kernel. Transfer learning was determined to be more effective when the number of source data with lower RMSPE was large. Furthermore, ARD made it possible to know the contribution of the individual parameters, and the contribution of parameters related to degradation damage was high.
- The seismic performance evaluation of a seismic isolation bridge pier considering the variation in the input earthquake ground motions was the second application considered for verification. This involved the surrogate modeling of nonlinear time-history analysis. It was shown that the effectiveness of TL was not as high as in the linear structural analysis in the first case; however, the TL-GPRSM was able to predict the distributions of the maximum displacements with slightly higher accuracy than the surrogate model without TL in some input cases.
- In nonlinear analysis, it was possible to determine the effectiveness of TL based on the magnitude of the contribution of the common part as estimated by the ARD kernel. The contribution of each parameter to the output estimated by the ARD kernel was reasonable from the viewpoint of nonlinear structural dynamics.
A future topic of study is the further consideration of surrogate modeling of nonlinear dynamic systems with effective TL. Further, the advanced DoE sampling that takes advantage of the estimated contributions in ARD is expected to reduce the computational cost of creating training data for effective TL. The selection of the kernel function in GPR with ARD is also worth considering, as the computational cost might be reduced by capturing the characteristics of the input–output relationship of the target numerical analysis appropriately. However, the results of this paper showed that the TL-GPRSM was effective in constructing the surrogate model of linear numerical calculations by reducing the computational cost of the structural performance analysis with linear numerical calculation under variation in uncertainties, such as the analysis of the damaged condition based on that of the undamaged initial condition. Moreover, it was shown that the effectiveness of TL in each surrogate modeling and the explainability of the constructed model could be discussed by deriving the contributions of each parameter by using the ARD kernel. This is significant in ensuring the acceptability of the constructed surrogate models in the structural performance evaluation for any decision-making.
Funding
This study was supported by the JST FOREST Program, Japan [grant number JPMJFR205T].References
- Bucher CG, Bourgund U. A fast and efficient response surface approach for structural reliability problems. Struct Saf 1990;7:57–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/0167-4730(90)90012-E.
- Kim S-H, Na S-W. Response surface method using vector projected sampling points. Struct Saf 1997;19:3–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0167-4730(96)00037-9.
- Zhao W, Qiu Z. An efficient response surface method and its application to structural reliability and reliability-based optimization. Finite Elem Anal Des 2013;67:34–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.finel.2012.12.004.
- Rocco CM, Moreno JA. Fast Monte Carlo reliability evaluation using support vector machine. Reliab Eng Syst Saf 2002;76:237–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0951-8320(02)00015-7.
- Roy A, Manna R, Chakraborty S. Support vector regression based metamodeling for structural reliability analysis. Probab Eng Mech 2019;55:78–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.probengmech.2018.11.001.
- Hawchar L, El Soueidy C-P, Schoefs F. Principal component analysis and polynomial chaos expansion for time-variant reliability problems. Reliab Eng Syst Saf 2017;167:406–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ress.2017.06.024.
- Marelli S, Sudret B. An active-learning algorithm that combines sparse polynomial chaos expansions and bootstrap for structural reliability analysis. Struct Saf 2018;75:67–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.strusafe.2018.06.003.
- Le V, Caracoglia L. A neural network surrogate model for the performance assessment of a vertical structure subjected to non-stationary, tornadic wind loads. Comput Struct 2020;231:106208. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compstruc.2020.106208.
- Chojaczyk AA, Teixeira AP, Neves LC, Cardoso JB, Guedes Soares C. Review and application of Artificial Neural Networks models in reliability analysis of steel structures. Struct Saf 2015;52:78–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.strusafe.2014.09.002.
- Deng J, Gu D, Li X, Yue ZQ. Structural reliability analysis for implicit performance functions using artificial neural network. Struct Saf 2005;27:25–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.strusafe.2004.03.004.
- Zhou T, Peng Y. Kernel principal component analysis-based Gaussian process regression modelling for high-dimensional reliability analysis. Comput Struct 2020;241:106358. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compstruc.2020.106358.
- Su G, Peng L, Hu L. A Gaussian process-based dynamic surrogate model for complex engineering structural reliability analysis. Struct Saf 2017;68:97–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.strusafe.2017.06.003.
- Gaspar B, Teixeira AP, Soares CG. Assessment of the efficiency of Kriging surrogate models for structural reliability analysis. Probab Eng Mech 2014;37:24–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.probengmech.2014.03.011.
- Avendaño-Valencia LD, Abdallah I, Chatzi E. Virtual fatigue diagnostics of wake-affected wind turbine via Gaussian Process Regression. Renewable Energy 2021;170:539–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2021.02.003.
- Rasmussen CE. Gaussian Processes in Machine Learning. In: Bousquet O, von Luxburg U, Rätsch G, editors. Advanced Lectures on Machine Learning: ML Summer Schools 2003, Canberra, Australia, February 2 - 14, 2003, Tübingen, Germany, August 4 - 16, 2003, Revised Lectures, Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer Berlin Heidelberg; 2004, p. 63–71. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-28650-9_4.
- Bichon BJ, Eldred MS, Swiler LP, Mahadevan S, McFarland JM. Efficient Global Reliability Analysis for Nonlinear Implicit Performance Functions. AIAA Journal 2008;46:2459–68. https://doi.org/10.2514/1.34321.
- Echard B, Gayton N, Lemaire M. AK-MCS: An active learning reliability method combining Kriging and Monte Carlo Simulation. Struct Saf 2011;33:145–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.strusafe.2011.01.002.
- Gaspar B, Teixeira AP, Guedes Soares C. Adaptive surrogate model with active refinement combining Kriging and a trust region method. Reliab Eng Syst Saf 2017;165:277–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ress.2017.03.035.
- Xiao N-C, Zuo MJ, Guo W. Efficient reliability analysis based on adaptive sequential sampling design and cross-validation. Appl Math Model 2018;58:404–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apm.2018.02.012.
- Zhou T, Marelli S, Sudret B, Peng Y. AK-PDEMi: A failure-informed enrichment algorithm for improving the AK-PDEM in reliability analysis. Mech Syst Signal Process 2022.
- Echard B, Gayton N, Lemaire M, Relun N. A combined Importance Sampling and Kriging reliability method for small failure probabilities with time-demanding numerical models. Reliab Eng Syst Saf 2013;111:232–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ress.2012.10.008.
- Huang X, Chen J, Zhu H. Assessing small failure probabilities by AK–SS: An active learning method combining Kriging and Subset Simulation. Struct Saf 2016;59:86–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.strusafe.2015.12.003.
- Moustapha M, Marelli S, Sudret B. Active learning for structural reliability: Survey, general framework and benchmark. Struct Saf 2022;96:102174. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.strusafe.2021.102174.
- Weiss K, Khoshgoftaar TM, Wang D. A survey of transfer learning. Journal of Big Data 2016;3:1–40. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40537-016-0043-6.
- Xiong Y, Guo L, Zhang Y, Xu M, Tian D, Li M. Surrogate modeling for spacecraft thermophysical models using deep learning. Neural Comput Appl 2022. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-022-07257-7.
- Kaya M, Hajimirza S. Using a Novel Transfer Learning Method for Designing Thin Film Solar Cells with Enhanced Quantum Efficiencies. Sci Rep 2019;9:5034. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-41316-9.
- Tian K, Li Z, Zhang J, Huang L, Wang B. Transfer learning based variable-fidelity surrogate model for shell buckling prediction. Compos Struct 2021;273:114285. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compstruct.2021.114285.
- Golparvar B, Papadopoulos P, Ezzat AA, Wang R-Q. A surrogate-model-based approach for estimating the first and second-order moments of offshore wind power. Appl Energy 2021;299:117286. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2021.117286.
- Williams C, Rasmussen C. Gaussian processes for regression. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 1995.
- Wipf D, Nagarajan S. A new view of automatic relevance determination. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 2007;20.
- Liu DC, Nocedal J. On the limited memory BFGS method for large scale optimization. Math Program 1989;45:503–28. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01589116.
- GPy. GPy: A Gaussian process framework in python since 2012. http://github.com/SheffieldML/GPy.
- Daumé H III. Frustratingly Easy Domain Adaptation. ArXiv [CsLG] 2009. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.0907.1815.
- McKay MD, Beckman RJ, Conover WJ. Comparison of Three Methods for Selecting Values of Input Variables in the Analysis of Output from a Computer Code. Technometrics 1979;21:239–45. https://doi.org/10.1080/00401706.1979.10489755.
- Nishio M, Miura M, Shuku T. Sparse Surrogate Modeling for Structural Reliability Analysis of Existing Bridges. Journal of Japan Society of Civil Engineers, Ser A2 (Applied Mechanics (AM)) 2018;74:I_125-I_136. https://doi.org/10.2208/jscejam.74.I_125. (in Japanese)
- Japan Road Association. SPECIFICATION FOR HIGHWAY BRIDGES PART II STEEL BRIDGES. Japan Road Association; 2012. (in Japanese)
- Japan Road Association. Handout on Seismic Design of Road Bridges [Translated from Japanese]. Japan Road Association; 1997. (in Japanese)
- Takeda T, Sozen MA, Nielsen NN. Reinforced Concrete Response to Simulated Earthquakes. Journal of the Structural Division 1970;96:2557–73. https://doi.org/10.1061/JSDEAG.0002765.
- Japan Road Association. SPECIFICATIONS FOR HIGHWAY BRIDGES Part V SEISMIC DESIGN. Japan Road Association; 2012. (in Japanese)